Note
Click here to download the full example code
Working with Time Series Data¶
This example shows how to load the included smartwatch inertial sensor dataset, and create time series data objects compatible with the seglearn pipeline.
Out:
DATA STATS - AGGREGATED
{'n_series': 140, 'n_classes': 7, 'n_TS_vars': 6, 'n_context_vars': 2, 'Total_Time': 4882.04, 'Series_Time_Mean': 34.87171428571428, 'Series_Time_Std': 8.757850351285423, 'Series_Time_Range': (18.94, 52.36)}
DATA STATS - BY CLASS
Class_labels n_series Total_Time Series_Time_Mean Series_Time_Std Series_Time_Min Series_Time_Max
0 PEN 20 532.44 26.622 2.720845 21.28 31.10
1 ABD 20 798.10 39.905 8.055554 22.48 49.10
2 FEL 20 809.96 40.498 8.772099 22.30 50.84
3 IR 20 747.90 37.395 9.085212 19.40 52.36
4 ER 20 752.08 37.604 7.983878 21.30 49.24
5 TRAP 20 611.56 30.578 6.099252 19.26 45.12
6 ROW 20 630.00 31.500 5.957100 18.94 38.66
/home/david/Code/seglearn/examples/plot_watchdata.py:67: UserWarning: Matplotlib is currently using agg, which is a non-GUI backend, so cannot show the figure.
plt.show()
# Author: David Burns
# License: BSD
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from seglearn.base import TS_Data
from seglearn.datasets import load_watch
from seglearn.util import check_ts_data, ts_stats
data = load_watch()
y = data['y']
Xt = data['X']
fs = 50 # sampling frequency
# create time series data object with no contextual variables
check_ts_data(Xt)
# create time series data object with 2 contextual variables
Xs = np.column_stack([data['side'], data['subject']])
X = TS_Data(Xt, Xs)
check_ts_data(X)
# recover time series and contextual variables
Xt = X.ts_data
Xs = X.context_data
# generate some statistics from the time series data
results = ts_stats(X, y, fs=fs, class_labels=data['y_labels'])
print("DATA STATS - AGGREGATED")
print(results['total'])
print("")
print("DATA STATS - BY CLASS")
print(pd.DataFrame(results['by_class']))
# plot an instance from the data set
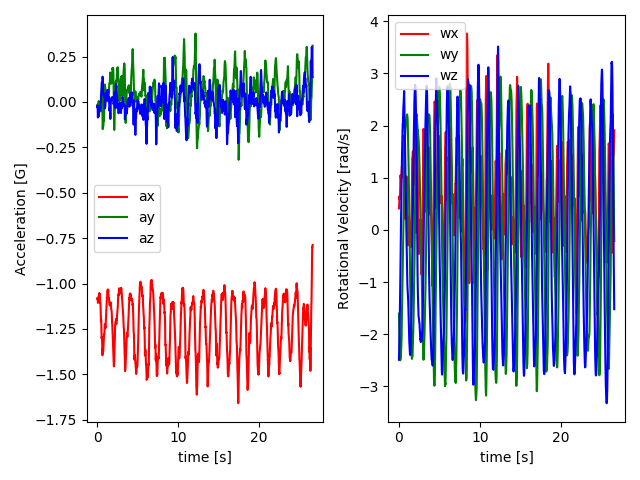
# this plot shows 6-axis inertial sensor data recorded by someone doing shoulder pendulum exercise
Xt0 = Xt[0]
f, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2)
t = np.arange(len(Xt0)) / fs
axes[0].plot(t, Xt0[:, 0], 'r-')
axes[0].plot(t, Xt0[:, 1], 'g-')
axes[0].plot(t, Xt0[:, 2], 'b-')
axes[0].set_xlabel('time [s]')
axes[0].set_ylabel('Acceleration [G]')
axes[0].legend(data['X_labels'][0:3])
axes[1].plot(t, Xt0[:, 3], 'r-')
axes[1].plot(t, Xt0[:, 4], 'g-')
axes[1].plot(t, Xt0[:, 5], 'b-')
axes[1].set_xlabel('time [s]')
axes[1].set_ylabel('Rotational Velocity [rad/s]')
axes[1].legend(data['X_labels'][3:6])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.209 seconds)