Note
Click here to download the full example code
Linear Discriminant Analysis¶
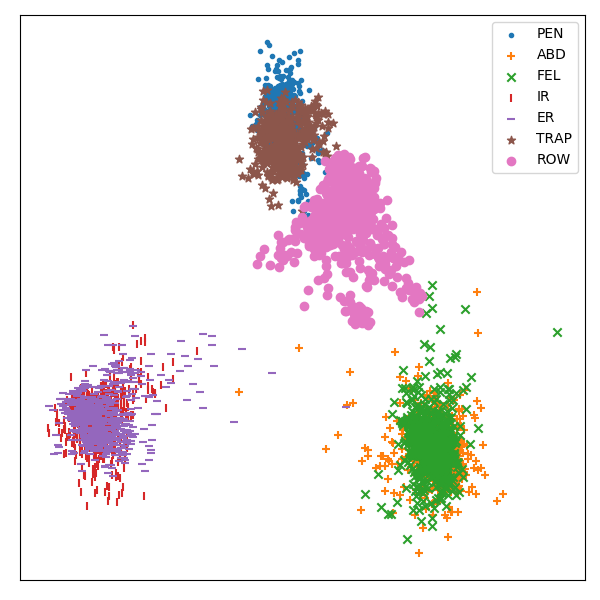
This example demonstrates how the pipeline can be used to perform transformation of time series data, such as linear discriminant analysis for visualization purposes
Out:
/home/david/Code/seglearn/examples/plot_lda.py:51: UserWarning: Matplotlib is currently using agg, which is a non-GUI backend, so cannot show the figure.
plt.show()
# Author: David Burns
# License: BSD
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis
import seglearn as sgl
def plot_embedding(emb, y, y_labels):
# plot a 2D feature map embedding
x_min, x_max = np.min(emb, 0), np.max(emb, 0)
emb = (emb - x_min) / (x_max - x_min)
NC = len(y_labels)
markers = ['.', '+', 'x', '|', '_', '*', 'o']
fig = plt.figure()
fig.set_size_inches(6, 6)
for c in range(NC):
i = y == c
plt.scatter(emb[i, 0], emb[i, 1], marker=markers[c], label=y_labels[c])
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
# load the data
data = sgl.load_watch()
X = data['X']
y = data['y']
# create a pipeline for LDA transformation of the feature representation
clf = sgl.Pype([('segment', sgl.Segment()),
('ftr', sgl.FeatureRep()),
('lda', LinearDiscriminantAnalysis(n_components=2))])
X2, y2 = clf.fit_transform(X, y)
plot_embedding(X2, y2.astype(int), data['y_labels'])
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.697 seconds)